Project Management with MindGenius
This guide is for those of you who haven’t ever used the words project management at work so we’ll try and start from the bottom and work our way up to explain everything that could be needed. Firstly, lets define what we consider to be a project – a project is a set of tasks grouped together with a common goal in mind that:
- Has a clear start and finish
- Creates something new (even if it exists elsewhere)
- Has boundaries including project scope and specifications
- Has someone in charge or someone personally involved in the outcome
Project Management is the process of delivering the project and the desired outcome within the defined timescales and agreed budget and is typically split into five key areas:
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Delivery
- Project Monitoring
- Project Closure
Project Initiation
A project will be kicked off to meet a specific requirement. Examples could include building a new website or implementing a new IT system – they are business needs that are outwith the normal business operations. At this point the nature and scope of the project will be outlined at a very high level – the detail will come later. At this stage it is important to understand what will be included in the project and importantly – what will not be included to avoid any confusion or doubt over the project scope and all stakeholders need to reach agreement on this.
The purpose of this is to gain agreement from stakeholders on the business need for the project as well as the feasibility before proceeding.
Once approval has been given for the project, the planning phase can begin.
Project Planning
During project planning, the high level scope agreed during project initiation is broken down into full requirements, objectives and deliverables and will include the preparation of a Project Scope Statement, a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Milestones, turning the WBS into a Gantt Chart, preparing a communication plan to let stakeholders know how you will update them throughout the duration of the project and a risk assessment into each area of the project.
With the breakdown of the work into individual tasks and a full project schedule prepared, dependencies are identified and the Critical Path of the project can be determined. Once this is complete the Project Baseline can be set. This will then be used to measure performance and progress against throughout the project.
Project Delivery
This is when the project kicks off, the individual tasks will begin and the team will get to work. Throughout project delivery, close attention should be paid to allocation of resources to identify any potential issues and bottlenecks that would impact on the overall delivery. Resources would refer to people working on the project as well as budget and materials.
Project delivery and project management and control are considered as separate phases of project management. However, in reality, these work hand in hand as monitoring goes on throughout the delivery of the project.
Project Monitoring
Monitoring throughout a project is hugely important and the delivery of the project should be monitored to a set of KPIs based on objectives delvierables, cost tracking and performance. Status meetings will take place throughout this phase and schedules will be altered as necessary.
It is important to keep documentation up to date throughout the project and that will also form part of monitoring and control. The baseline taken at the beginning of the project will be measured against throughout to highlight areas where the actual delivery differs from the original plan. This provides an opportunity to highlight potential red flags and major concerns so these can be addressed at the time and aren’t ignored until the due date and then come as a nasty surprise to everyone.
Project Closure
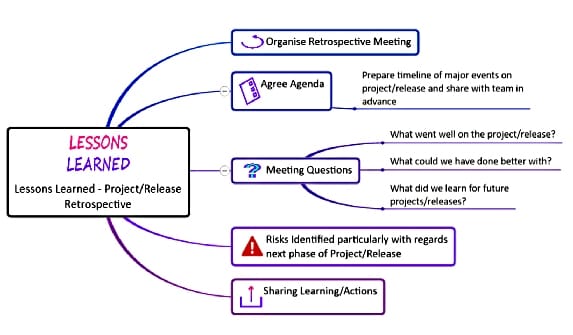
By it’s nature a project will reach a completed state and the end result will be delivered. A final project report will be completed and a post project close out meeting review should be held – this will focus on what worked, what didn’t and lessons learned for the future.
MindGenius For Project Management
MindGenius enables users to capture, visualise and use information to deliver successful projects. Get your project off to the right start by fully understanding requirements, agreeing project scope and preparing your work breakdown structure before seamlessly converting your plans into a Gantt chart to manage individual tasks and monitor your project to successful completion. View this short 2 minute video on how MindGenius can take your project from idea to delivery.
Project Phases with MindGenius
Project Initiation
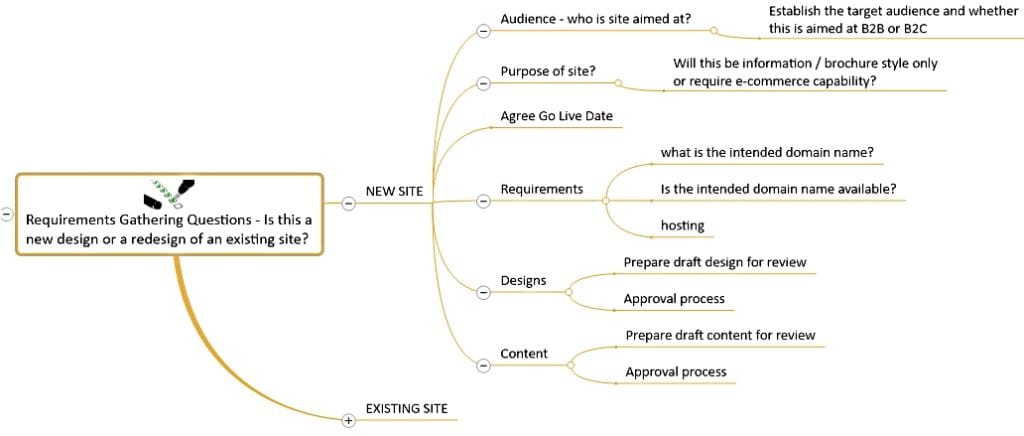
In this example, we use building a new website as an example of a project:
To kick that off in MindGenius, the project planning would begin by capturing all of the requirements for the project in a mind map. This can be done by one person or come together as a group to brainstorm ideas for the project. This is then used as a basis for a project kick off meeting with the key stakeholders to ensure everyone is on the same page before moving to the more detailed project planning stage.
Project Planning
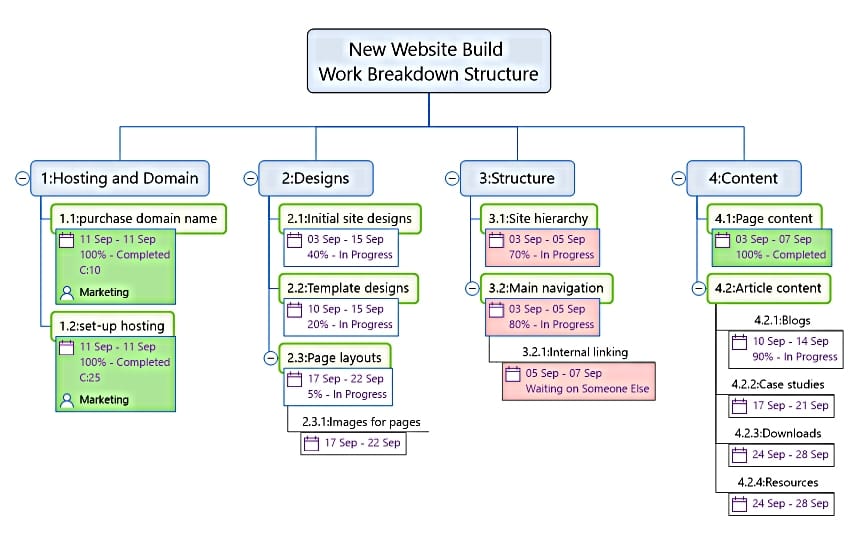
The information gathered during the project initiation stage can be turned into specific tasks by creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in MindGenius where you can detail the deliverables, work packages and activities which will be required to deliver the project. The WBS will also include the related costs and resources which will be involved. MindGenius enables you to add numbering to your WBS to display each level of activity level and overall for the full project.
At this planning stage, you can prepare your Project Scope Statement in MindGenius by detailing:
- the full scope description of the project
- the list of deliverables
- user acceptance criteria – the critical success factors
- boundaries to the project – a list of things that are outwith the scope of this project
- project constraints such as timescales, costs, technical issues
- project assumptions – a list of things thought to be correct but aren’t confirmed
All of these points are set out in the scope statement and agreed to by all stakeholders. This agreement means this can be referred back to at any point throughout the project is discussions arise on tasks felt to be outwith the original scope agreement.
Taking all of the project detail and turning it into a Gantt Chart is seamless in MindGenius. Switch to this view to see the full project plan, as well as the critical path and project milestones. The project baseline can be taken at this point in the form of a snapshot which can be used to measure progress moving forward. Up to 10 snapshots can be taken in MindGenius during the project and can be overlaid on the actual schedule to monitor progress.
Project Delivery & Monitoring
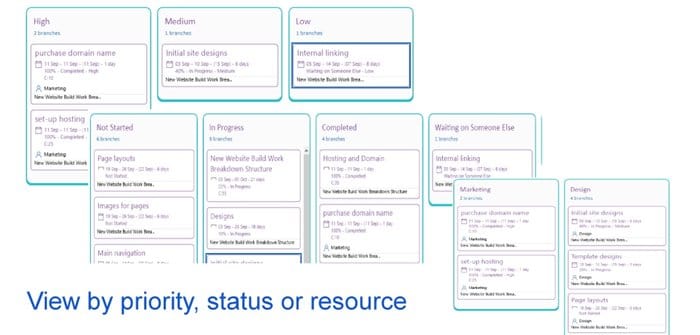
When it comes to the delivery of the project, MindGenius can keep you on track with the ability to update task and resource information. This can be used to report status and shared at status meetings. The snapshot overlay functionality gives views of progress against the original plan and if the project is on target or ahead or behind schedule.
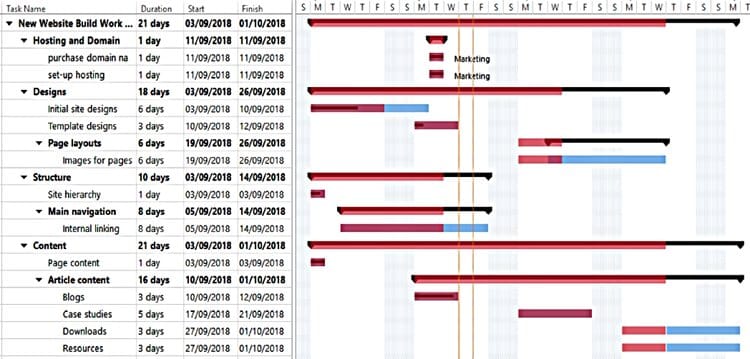
Dynamic views provide different perspectives of the same information, depending on how you want to view certain details. Choose to view by resource, category, priority or status.
Project Closure
On completion and handover of the project deliverables, MindGenius can be used to store final documentation and to run the project close out meeting, capturing lessons learned in MindGenius for follow up and action when needed.
MindGenius can be used at every stage of your project to keep you on track. Download a 14 day free trial to learn how our products can help you deliver projects that are on time and on budget.